SESSION Layer in OSI Model
The Session layer is the fifth layer in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model. It plays a crucial role in managing and controlling the dialog between two computers, establishing, maintaining, and terminating communication sessions.
The tasks performed are:
1.Session Establishment, Maintenance, and Termination
2.Synchronization
3.Dialog Control
4.Session Recovery
5.Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA)
What is Session Establishment, Maintenance, and Termination?
– Establishment: Initiates connections between applications on different devices, ensuring that communication sessions are properly started.
– Maintenance: Keeps the session alive and manages the data exchange, ensuring that the connection remains open and functional.
– Termination: Properly closes the session once communication is complete, freeing up resources.
SESSION LAYER:
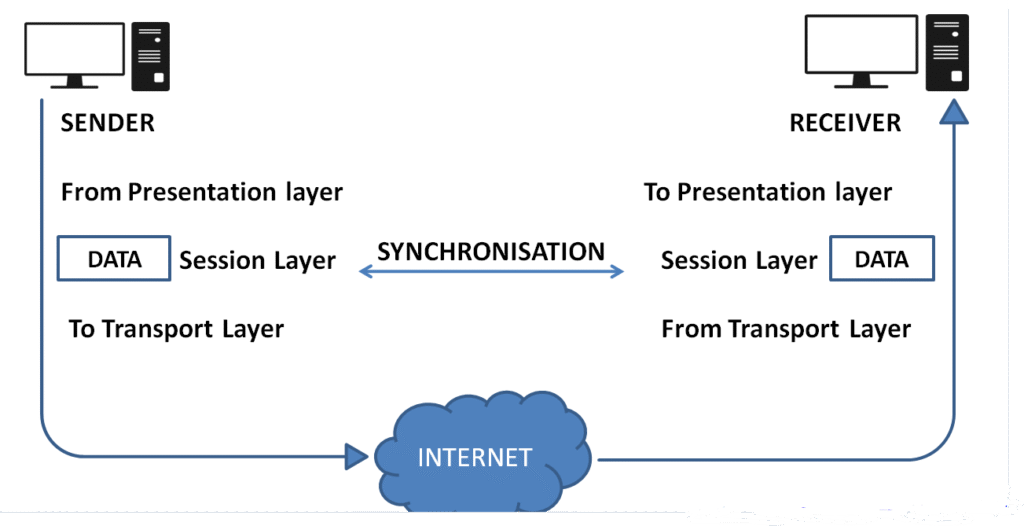
Synchronization:
– Manages synchronization points, or checkpoints, within a stream of data. If a session is interrupted, these checkpoints allow the session to be resumed from the last checkpoint rather than starting over.
– This ensures data integrity and continuity, particularly important for long communications or large data transfers.
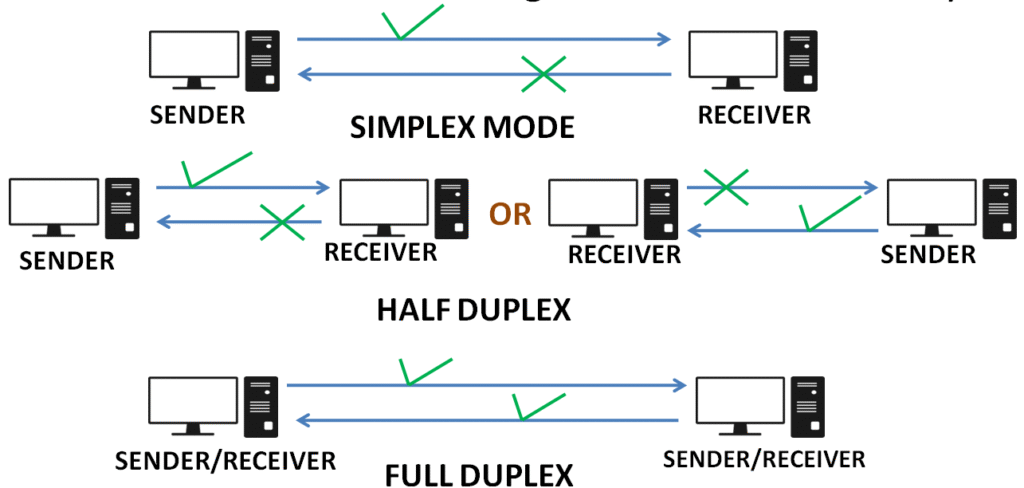
Dialog Control:
– Controls whether the communication is in half-duplex or full-duplex mode.
– Half-Duplex: Allows data transmission in one direction at a time.
– Full-Duplex: Allows simultaneous data transmission in both directions.
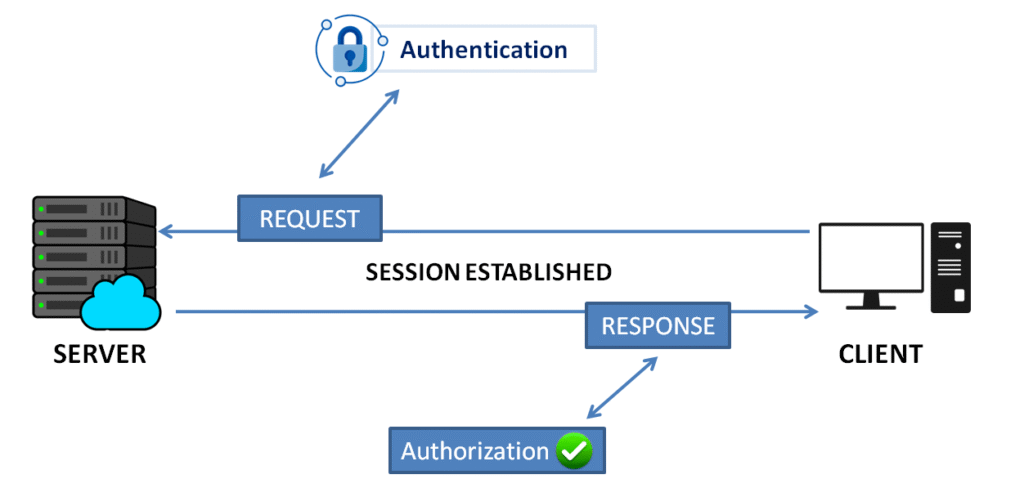
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting (AAA):
Authentication: Verifies the identity of users and devices attempting to establish a session. Ensures that only authorized entities can initiate communication.
Authorization: Determines whether an authenticated user has permission to access the requested resources or perform certain operations during the session.
Accounting: Tracks the usage of network resources by users and devices, often for auditing, billing, or resource allocation purposes.

Ravish Safi
Technical Trainer for Networking

